Cyber security has been a consistently growing field in the tech space as cyber-attacks become more sophisticated and frequent. Cyber security professionals help organizations protect their company data and systems, including hardware and software.
Interested in a budding career as an information security analyst, or maybe even a cyber security director? We’ve rounded up the top cyber security interview questions you’re most likely to hear in 2024, including for beginner, intermediate, and advanced professionals.
Cyber Security Interview Questions and Answers for Beginners and Experienced Professionals
Let’s start with the basics in our first section of information security interview questions:
Basic Cyber Security Interview Questions for Freshers
1. What is cryptography?
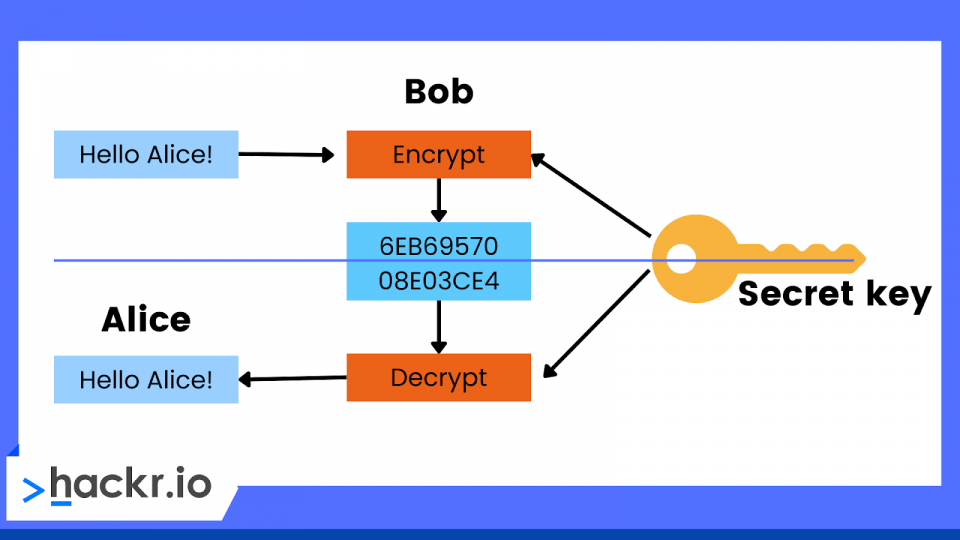
Cryptography assures secure communication even with malicious outside actors or adversaries. An algorithm and a key are used in encryption. The key converts plaintext from input into an encrypted output (i.e., cipher text). The same plaintext will always be converted into the same ciphertext if the same key is used, according to a particular algorithm.
2. How do IDS and IPS differ from one another?
The administrator must stop incursion once the IDS, or intrusion detection system, discovers them. Contrarily, in an IPS (intrusion prevention system), the system not only detects the intrusion but also addresses it.
3. How is encryption different from hashing?
Hashing and encryption change one type of data into another. Encrypted data can be decrypted and converted to the original, while hashed data cannot be reconverted.
4. Why do organizations use firewalls? What does it do?
A firewall is a type of network security device installed on a system or network perimeter. It monitors and manages network traffic. Cyber security professionals use firewalls to safeguard systems and networks from malware, worms, and other threats. They also allow you to block content filtering and remote access.
5. Describe the three-way handshake.
A three-way handshake is a procedure used in a TCP/IP network to establish a client-host connection and exchange packets. Here’s the three-step procedure:
- The client sends an SYN (synchronization) to check for available ports and whether the server is online.
- If the client has open ports, the server will send an SYN-ACK message.
- The client acknowledges the message and returns an ACK(Acknowledgment) packet to the server.
6. Describe traceroute. Why is it employed?
A traceroute displays a packet’s path. It lists every location the packet passes through, primarily routers, especially when a packet doesn't get to its destination. Finally, traceroute helps you determine where the connection drops or breaks.
7. What distinguishes HIDS and NIDS from one another?
Both HIDS (Host IDS) and NIDS (Network IDS) are intrusion detection systems that find intrusions. Programmers employ the HIDS on a specific host or device — the only distinction. It keeps an eye on a device’s suspicious system activity and traffic. However, NIDS is configured on a network. It keeps track of every network device’s traffic.
8. What are the possible response codes for a web application?
Here are some possible response codes for a web application:
- Informational responses
- Server-side error
- Redirection
- Client-side error
- Success
9. What is the CIA triad?

CIA stands for Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. Businesses often use CIA models to direct information security policy.
- Confidentiality
Only authorized personnel should be able to access and view the material. Strong encryption protects the data so that even if a hacker obtains it, they won’t be able to comprehend it.
- Integrity
Integrity guarantees that unauthorized individuals cannot corrupt or modify data.
- Availability
The data must be available to the user whenever they need it. Availability is crucial to address network bottlenecks, regular upgrades, data backups and recovery, and device maintenance.
10. What distinguishes penetration testing (PT) from vulnerability assessment (VA)?
Vulnerability assessment is a process for finding target faults. In this case, the organization is aware that its systems or networks have defects or weaknesses, and they want to identify these flaws and prioritize them.
Meanwhile, penetration testing is a process for finding vulnerabilities. In this scenario, the firm would have installed all security precautions they could think of and would wish to investigate any more vulnerabilities in their network or system.
11. What procedures are involved in installing a firewall?
Here are the steps to install a firewall:
- Username/password: Change a firewall device's default password
- Remote administration: Turn off the remote administration feature.
- Port forwarding: Set up the proper port forwarding to ensure applications like a web or FTP server function properly.
- DHCP server: Disable the firewall’s DHCP server to ensure no conflict.
- Logging: Enable logging and learn how to view logs to fix firewall problems or potential assaults.
- Security policies: Establish strong, enforceable security policies for your firewall.
12. How does the SSL protocol guarantee network security?
The SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) authenticates the sender and establishes secure connections between the browser and web server. Still, it does not offer security once the data has been sent to the server. That’s why server-side encryption and hashing are necessary to guard against data breaches.
Here’s the general procedure for establishing an SSL connection:
- A browser tries to establish a connection with an SSL-secured web server.
- A copy of the browser's SSL certificate is sent to the browser.
- The browser verifies the SSL certificate's trustworthiness. If it is reliable, the browser notifies the web server that it wants to create an encrypted connection.
- The web server transmits an acknowledgment to create an SSL-encrypted connection.
- The web server and browser communicate using SSL encryption.
Suggested Course
Cyber Security: From Beginner to Expert (2024)
13. How can you secure a server?
Secure servers encrypt and decode data using the Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocol to prevent unauthorized access to it.
Here are four fast ways to safeguard a server:
- Step 1: Make sure your root and administrator account passwords are safe.
- Step 2: Create new users to manage the system.
- Step 3: Ensure the root and administrator accounts cannot access the internet by default.
- Step 4: Configure your firewall rules for remote access.
14. What do you know about data leakage?
Data leakage is a purposeful or unintentional transmission of data (private information from within the company to an unapproved outside location (unauthorized party).
Based on how it occurs, we can split data leakage into three categories:
- Accidental Breach: When an organization accidentally sends information to a third party due to a mistake or error.
- Intentional Breach: When an authorized entity sends data to an unauthorized party on purpose.
- System hack: A hacker accesses private data.
You can stop data leakage with DLP (Data Leakage Prevention) tools, software, and techniques.
15. What is a brute force attack? What can you do to stop it?
Brute force is a method for accessing credentials by trial and error — continually attempting all possible combinations of credentials until you hit the right one. Here’s how you can avoid brute force attacks:
- Maximum Length Password: Specify the maximum length of a password, so it becomes harder to find the right combination.
- Password Complexity: Requiring many character types in the password makes brute force attacks more difficult. You might establish requirements for special characters, upper- and lower-case letters, and numbers.
- Limiting Login Attempts: Establish a cap on failed login attempts, which makes it impossible to try all possible password combinations.
16. Why do ports get scanned?
Port scanning is a technique to determine a host’s available and open ports. Hackers use it to exploit vulnerabilities, while administrators use it to check the network's security procedures.
Common methods for port scanning include:
- Ping Scan
- TCP Half-Open
- TCP Connect
- UDP
- Stealth Scanning
17. What are the OSI model layers?

The OSI model serves as a standard for how applications communicate with one another over a network. An OSI reference serves as a roadmap for suppliers and developers to ensure digital communication hardware and software interoperability.
The OSI layers are as follows:
- Physical layer: Digital data transmission from sender to receiver via a communication medium.
- Data Link Layer: Encodes and decodes data bits and controls data transfer to and from the physical link.
- Network Layer: Forwards packets and offers routing channels for network communication.
- Transport Layer: Ensures end-to-end network connection by dividing the data from the layer above, sending it to the network layer, and verifying the recipient received all the data.
- Session Layer: Establishes and manages a session-layer connection between the sender and the recipient. In addition to starting, halting, and controlling the session, it is responsible for establishing, maintaining, and synchronizing contact between the sender and the receiver.
- Presentation Layer: Displays the data in a suitable manner and structure.
- Application Layer: Interface between the network and the application, emphasizing process communication on a communication interface.
Intermediate Cyber Security Questions and Answers
18. What is a VPN?
The majority of cybersecurity interview questions will include this one. VPN stands for virtual private network, which creates a safe, encrypted connection. A VPN enables the client's data to be forwarded to a tunnel location for encryption before delivery to another location. The data has now been transmitted to the server after being decrypted.
19. What does it mean for a network to have risk, vulnerability, and threat?
- Threat: Someone who poses a threat to a system or an organization
- Vulnerability: A flaw in a system that a potential hacker could use
- Risk: Possibility of damage or loss if a threat takes advantage of a weakness.
20. What do "white hat," "black hat," and "gray hat" hackers mean?
- Black-hat hackers are renowned for having an extensive understanding of entering computer networks. They can create malware that allows users to access these systems. These kinds of hackers abuse their abilities to steal data.
- White-hat hackers are ethical hackers since they employ their skills for good reasons. Businesses frequently employ them as security specialists who look for and close security gaps and vulnerabilities in their systems.
- White-hat and black-hat hackers combinedly form gray-hat hackers, who search for vulnerabilities without the owner's consent. They notify the owner if they discover any weaknesses. In contrast to black-hat hackers, they don't use the vulnerabilities discovered.
21. Describe the distinction between a cryptographer and a crypter.
A cryptographer plans or analyzes any aspect of encryption.
On the other hand, a crypter deliberately disguises malware as something else, such as a useful program, to propagate it unnoticed.
22. What are a few important applications of cryptography in contemporary society?
There are several advantages to using cryptography, like:
- Chip-based installment cards
- PC and different passwords
- Internet business
- Guard interchanges
- Computerized currencies
- Planning conventions
- Information credibility
23. What are the main threats to any information or data that requires cryptography?
There are a lot of risks, and you could not be aware of them. As for the advancement of innovation, the knock-on effects of the same have also been enhanced everywhere. Programmers have access to information, and any leaked sensitive information can cause problems for a company, an administration, or a financial institution, as well as for a single person. The association may be in jeopardy if private data is compromised.
24. How would you describe secret key and public key cryptography? What distinguishes them from one another?
Both secret and public key cryptography contribute to information security by performing encryption calculations. Secret key cryptography can encode and decode the two encryptions.
However, public key cryptography effectively employs a symmetric methodology. This system uses two keys, one of which is effectively the public key, making the data accessible to any client. The key is secure and can only be obtained by the director.
25. When is a cryptographic shrinking generator required?
You can use a cryptographic shrinking generator when there needs immediate cooperation on the outcomes of linear feedback shift registers. It has excellent securing qualities and is generally adaptive, making it a good technique for handling trust. You can also use it to research data collection methods.
26. What distinguishes encryption from decryption?
Encryption converts plain text into ciphertext, while decryption converts ciphertext into plain text.
27. What is SSH?
SSH (Secure Shell) is the less complex and expensive network connection that hardware-based VPN solutions offer.
With SSH, we may access a variety of TCP/IP apps remotely and securely through a secure tunnel and benefit from secure command-shell and file transfer functionality. It offers additional advantages like pre-encryption compression, which may significantly reduce data encryption computational costs, and host authentication and data encryption & integrity.
28. What are ports?
Ports are an abstraction that allows programs to communicate via different protocols. We use them with transportation layer protocols like TCP, UDP, and SMTP.
Different services are given a port number. For instance, HTTP uses TCP and UDP port 80. A pair of systems opens many sockets using the same transport protocol by employing port numbers.
29. What is an IP address?
An IP address is a specific identifier for a computer or device connected to the internet or a local network. "Internet Protocol" (abbreviated as IP) is a set of guidelines that control the format of data supplied across a local or public network. A series of digits separated by dots forms an IP address. Each IP address block is shown as a four-digit permutation, such as 192.158.1.38.
The range of possible values for any integer in the set is 0 to 255. The entire IP addressing range is therefore 0.0.0.0 to 255.255.255.255. Each device is given an IP address by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA), a division of the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN).
30. How is a static IP address different from a dynamic IP address?
Dynamic IP address
Your ISP permits you to use a dynamic IP address on a temporary basis. A dynamic address may be assigned to another device if it is not already in use. IP addresses are assigned dynamically via DHCP or PPPoE.
Static IP address
Static IP addresses remain constant over time. If you have a web server, FTP server, or other internet resources requiring a set address that shouldn't change, you can obtain a static IP address. An manually configured static IP address is required.
31. What is IPv6?

In the Internet Protocol Version 6 (IPv6) addressing model, a 128-bit alphanumeric string known as an IPv6 address identifies an endpoint device.
An IPv6 address is really made up of eight 16-bit groups, totaling 128 bits in length. Each group has four hexadecimal digits that serve as its representation, and colons are used to separate groups.
The IPv6 standard was created to connect not only an expanding number of computing devices but also an expanding number of items with embedded connections.
In a scenario of the Internet of Things (IoT), inanimate objects, living things, and people all have the ability to independently exchange data via a network without the requirement for human-to-human or human-to-computer interaction.
32. What is a botnet?
A botnet is a collection of computers infected with malware, and controlled by an attacker to carry out some background tasks to attack a specific target. For instance, the attacker might use all of the infected computers to speed up a dictionary attack on another system.
33. What is CSRF?
CSRF stands for cross-site request forgery attack, where a victim is tricked into carrying out the attacker's instructions. Depending on the victim's degree of permission, the attack's effect will vary. Such attacks profit from the fact that when a user's identity has been verified, a website automatically trusts them.
A CSRF requires two basic steps for execution:
First, the hacker dupes the target into opening a page or clicking on a link. Typically, social engineering and fraudulent links are used to do this. Next, the victim's browser makes an artificially convincing request to the website.
34. What is 2FA?
2FA stands for “two-factor identification.” It’s the second security layer that ensures anyone attempting to log into an online account is who they claim to be. First, the user must provide their username and password.
Then, they must offer another piece of information, usually a code sent through email or another device.
35. What is cross-site-scripting?
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is an injection where an attacker inserts script (typically Javascript) onto a page, and it essentially functions as if the administrators had created it themselves.
A hacker can have total power to change the display, tweak the browser, or even steal your session cookie and sign in as an administrator with XSS.
36. What is network sniffing?
Network sniffing intercepts data packets sent over a network.
37. Describe the salting procedure and its purpose.
Salting employs special characters to lengthen and protect passwords. Additionally, it stops attackers from scanning the system for recognized words.
38. Describe the weaknesses in network security.
Vulnerabilities are the weak spot in software code that a threat actor could attack. They are most frequently discovered in SaaS.
39. What do you understand about the term forward secrecy?
Forward secrecy is an attribute of key agreement protocols, which assures that even if the server’s private keys are exposed, sessions will not be exposed. It is also referred to as the perfect forward secrecy.
40. What is penetration testing?
Penetration testing assesses and enhances an organization’s security system, network, or data center. Ethical hackers will seek out vulnerabilities and attempt to penetrate the system to improve security standards.
41. How can user authentication be made to be more secure?
You can make user identification more secure by requiring an ID and Key, as well as 2FA.
42. What is a worm?
A worm is a type of malware that spreads from computer to computer.
43. What dangers come with using public Wi-Fi?
Public Wi-Fi security is a serious concern. Wi-Fi assaults might include snooping, war-driving, brute-force attacks, and more. Public Wi-Fi may identify data transported across a network device, such as emails, browser history, passwords, and credit card information.
44. What is the definition of remote desktop connection?
You can take complete control of another computer using a remote desktop connection.
45. What is a buffer overflow attack?
A buffer overflow attack is a process that tries to write extra data to a fixed-length memory block.
46. What is spyware?
Spyware is software intended to remain undetected while tracking and recording your online activities and reporting that activity to remote control. Spyware can be either software or hardware, and it's frequently installed as Trojan malware that impersonates another program. As hardware, it could take the form of a keylogger-like device connected to a computer or network that records data flow, online movements, or user names and passwords.
47. What is a computer virus?
A computer virus is malicious software that infects and takes control of computers. You should be cautious while opening attachments and clicking on links in unsolicited messages to avoid computer viruses. Trojan horses, overwrite viruses, and web scripting viruses are a few computer virus examples.
48. What is CryptoAPI?
CryptoAPI helps developers build projects on a secure network.
49. What is ethical hacking?
Ethical hacking identifies system or program vulnerabilities to prepare for cyber-attacks.
50. What are some popular hacking tools?

Some popular hacking tools include:
- Netsparker
- Angry IP scanner
- Savvius
- Burp Suite
- Acunetix
Bonus Tips
If you need to recollect cyber security’s basic and advanced concepts, review these comprehensive cyber security interview questions and answers. But you don’t have to stop there.
Here are some bonus tips to ace your next cybersecurity interview:
- Prepare for scenario-based interview questions. Leverage the STAR (Situation, Task, Action, and Result) technique. Simply collect your views, and present an answer that explains the situation and the result.
- Try mock interviews. Practice our list of security analyst interview questions with a friend!
- Update your resume. Completed a recent cyber security project, or finished an internship? Make sure to add anything you Keep your resume updated.
- Be confident. You’ve studied hard and prepared well for your interview. Don’t doubt yourself!
Conclusion
These top cyber security interview questions are a fantastic way to feel confident and prepared for your next interview. But you don’t need to stop there — cyber security college programs, boot camps, certifications, and even tutorials cover topics like databases, web technologies, cryptography, network, computer viruses, and more.
Furthering your education is a great first step to preparing for network security interview questions.
People are also reading:
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How Do You Do a Good Cyber Security Interview?
You should be well-versed with major computer science-related topics, like Web Technologies, DBMS, Cryptography, and mathematics, along with some hands-on experience with cyber security tools.
2. What Are the 3 Major Types of Cyber Security?
The three major types of cyber security are:
-
Application security
-
Network security
-
Cloud Security
3. What is Phishing in Cyber Security?
Phishing is a form of social engineering where an attacker delivers a false message to dupe an authorized user into giving up personal information. This enables the attacker to install harmful software, such as ransomware, on the victim's computer.
4. Is Cyber Security Easy or Hard?
Learning cybersecurity can be challenging without any programming knowledge. However, you can choose from endless tutorials and courses to prepare for a cyber security career.
People Are Also Reading:
- Security Testing Tools
- Hacking Books
- Cyber Security and New Technologies
- Types of Software Testing
- Cyber Security Certifications
- What is Selenium?
- Top Selenium Interview Questions & Answers
- Selenium IDE: A Complete Guide
- Top Manual Testing Interview Questions
- Best Blockchain Courses
- What is Cloud Computing?
- What is IoT Security?
