Chances are that in 2024, you’ve heard of cloud computing services, whether that’s Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform, and that’s just the big hitters.
It’s estimated that by 2025, the world will store 200 zettabytes of data, with 50% on the cloud. That’s not to mention that public spending on cloud computing has seen year-on-year growth from $145 Billion in 2009 to nearly $600 Billion in 2024.
Cloud computing is on the rise, with more and more individuals and organizations making the switch or adopting a hybrid cloud solution. But why are so many adopting cloud technology?
In this article, we’ll explore the top 10 benefits of cloud computing, along with a short discussion of its limitations and speculations about the future of cloud technology in 2024 and beyond.
If you’re new to the cloud and you’d like to build a strong foundation in cloud skills from various cloud providers and platforms, we highly recommend IBM’s introduction to cloud computing.
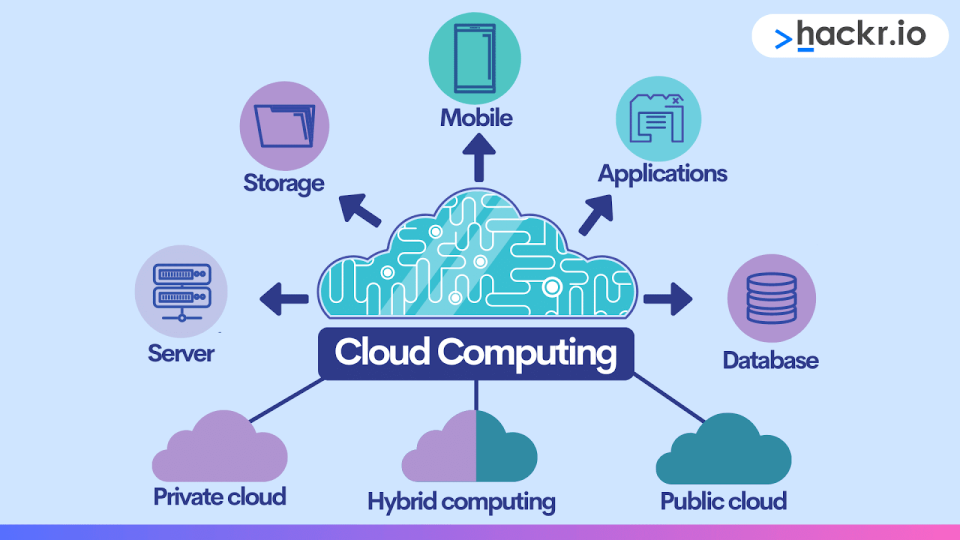
What Is Cloud Computing?
What is cloud computing? Let’s start with the definition of the cloud.
A cloud is a network of powerful servers and computers located in various data centers in many different locations (sometimes worldwide). These data centers are typically managed by vendors, including giants like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft.
Due to the vast amounts of data handled on the cloud, data centers typically have massive amounts of processing power, storage space, and other resources.
When you save something to the cloud, it means you're storing it on those remote computers rather than on your local device. You can upload your files to the cloud, and they will be securely stored and accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
In general, when we use the term “cloud computing”, we’re describing the on-demand delivery of computing resources over a network (typically the Internet), whether those resources are storage, hardware, networking, databases, or software.
Put simply, cloud computing provides individuals and organizations with on-demand access to a shared pool of computing resources, including servers, storage, databases, networking, and software applications, over the Internet, all without having to manage any physical infrastructure in-house.
The Top 10 Benefits of Cloud Computing
What are the benefits of cloud computing? Well, you’ll often hear that it offers reduced costs, improved accessibility and mobility, innovation, sustainability, or advanced security.
To pain a better picture of this concept, we’ve covered the top 10 cloud technology benefits below.
1. Cost Savings
One of the main cloud advantages that people focus on is the potential for cost savings. This is because cloud computing allows you to reduce or eliminate purchase and maintenance costs for physical hardware and infrastructure.
Yet the biggest benefit regarding cost is usually the ‘pay-as-you-go’ pricing model that most cloud vendors implement.
This means that you only need to pay for the resources you use, allowing individuals and organizations to optimize costs while avoiding the pitfalls of overbuilding, overprovisioning, and overinvesting in data center hardware.
2. Flexibility & Scalability
Another benefit of cloud computing is the flexibility and ability to scale resources up and down as demand requires.
This allows organizations to respond to everchanging market conditions in a timely manner, avoiding the costs of investing in and maintaining underutilized data centers and resources. At the same time, companies can rapidly scale up, should they experience a sudden spike in traffic or demand.
Cloud computing is renowned for offering high performance and availability, often at a lower cost than in-house infrastructure. That said, companies can also adopt hybrid setups, where on-premise and cloud solutions are used in tandem, offering the best of both worlds.
In fact, hybrid setups are often the first step that very large organizations take into the world of cloud computing. This allows them to extract the maximum value from any existing investments into their own, typically expensive, on-premise infrastructure.
This also allows companies to migrate over to the cloud at a pace that feels comfortable, which can be especially important when there are strict data control regulations that they need to adhere to.
3. Mobility & Accessibility
Accessibility and mobility are one of the best cloud computing advantages, as users can access data and applications anytime and anywhere with an internet connection.
Cloud computing is practically a necessity for organizations with hybrid or remote workers, as it makes data conveniently accessible for employees and stakeholders.
Cloud computing also enables users to access applications on devices and machines that would otherwise be unable to run them. It provides access to tools and materials that would not have been available otherwise, which is why it’s becoming more popular in education and online learning.
4. Advanced Security
Improved security is another of the top cloud service benefits today. Cloud computing vendors typically install and use advanced security measures to help ensure customers’ data and applications are protected.
Cloud vendors typically use a wide range of centrally-managed and well-maintained security features to keep malicious actors at bay, prevent bot attacks, secure apps and data, and more. According to our research, these companies hire thousands of cyber security experts — just look at Microsoft, which hired 3,500+ professionals to keep Azure secure.
Cloud security is now a field in and of itself, having emerged as an essential response to the needs of more and more companies adopting cloud technology. It’s even possible to recruit the services of cloud security companies to monitor applications, encrypt data, and detect breaches, further improving your data privacy and security.
5. Innovation
Ideas are free, but not everyone has the resources to bring those ideas to fruition. Cloud computing can level the playing field, making resources accessible without the cost-prohibitive initial investment.
Access to new tools and technology helps users and organizations innovate, providing room for ingenuity without the high upfront costs that would have been required otherwise.
A great example is the ability to implement serverless solutions, regardless of budget or the size of the enterprise. This cloud-based innovation allows anyone to infinitely scale their computing power to handle a range of technical challenges, demonstrating how the cloud has created a level playing field.
Cloud computing can also give businesses a competitive edge, offering increased convenience, lowered costs, improved security, improved collaboration, and more. Suffice to say the concept of innovation is intrinsically tied to the cloud, which itself is a beacon of innovation.
6. Faster Time to Market
Another of the fantastic benefits of cloud services is that end users can potentially speed up development time, in turn reducing the time it takes to get their product to market.
In our experience, cloud computing takes care of the hardware infrastructure, eliminating time spent waiting for hardware procurement and deployment.
Cloud computing also makes containerization via services like Docker more convenient. And with the huge growth in microservices, containerization, and cloud computing have become perfect partners.
Just in case you’re not familiar with containerization, this allows apps to be packaged with all of their necessary files, dependencies, and libraries into a single container, which is an excellent way to logically separate multiple apps that can run on a single server without conflict.
7. Improved Collaboration
Cloud computing can boost efficiency and overall productivity because it provides easy access to shared files, compute resources, networks, and more.
In general, cloud collaboration enables real-time editing, commenting, asynchronous communication, and more, thus providing flexibility to work anytime and anywhere — sometimes even on a mobile device!
Many cloud services offer features like access control (permissions) to improve security, along with version control to monitor changes as they happen, offering the option to revert changes if needed.
Google Workspace is an excellent example of collaboration through cloud computing.
8. Data Loss Prevention & Disaster Recovery
Cloud storage is hugely beneficial for preventing data loss due to hardware malfunctions or malicious actors. The cloud can even guard against simple user error, adding an extra layer of protection in that regard.
Most cloud vendors offer features to help prevent data loss and related disasters. For example, many cloud providers provide features that allow and even automate backups, making it possible to recover data quickly in the event of a problem.
Many may choose to store their data in the cloud while keeping a copy on physical hardware as a contingency (or vice versa).
9. Insights & Analytics
Cloud computing has also made a massive impact on business intelligence, as it provides real-time access to business data to help organizations identify trends, analyze supply chain/production data, optimize processes, set business goals, and more.
This real-time access makes it possible for data analysts to work with tools, software, and methodologies that provide executives and stakeholders with meaningful insights.
Cloud services also enable businesses to make data-driven decisions in a timely manner, which is vitally important in rapidly changing market conditions.
Many cloud services also offer integrated analytics that provides an overview of what’s going on with your data and services, which can help you optimize your cloud usage.
10. Sustainability
It’s hard to find any argument against modern practices that make an effort toward sustainability.
One immediately apparent benefit of cloud computing is the reduced need for hardware components and related materials for establishing, maintaining, and upgrading on-premise infrastructure.
This can make a significantly positive impact on the environment, especially considering the elimination of many large-scale data centers that have moved to the cloud.
On-premise infrastructure can be incredibly power-hungry, especially considering the added energy costs of running cooling systems. Cloud computing can potentially reduce energy consumption and costs here.
Cloud vendors can also further sustainability efforts by switching to renewable energy. The big three (AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure) are taking remarkable steps in this realm, with AWS and Azure pledging to run on 100% renewable energy by 2025.
Google Cloud Platform, on the other hand, has already declared itself carbon neutral, with ambitions to be fully carbon-free by 2030.
Although it’s challenging to tell whether cloud vendors are truly succeeding in achieving sustainability, our research finds that they are at least making the effort in this regard.

What Are the Limitations of Cloud Computing?
Despite the many advantages of cloud computing, there are some limitations to keep in mind. After all, although cloud technology can benefit individuals, businesses, and organizations, it’s not infallible.
One of the primary disadvantages is the reliance on an internet connection, meaning that connectivity issues of any kind may impact access to data, applications, services, and more.
Of course for larger organizations, it is possible to invest in dedicated connections to their cloud vendor’s data center, but for smaller organizations and individuals, this is not usually possible.
Let’s take a look at some more potential limitations and disadvantages of cloud computing:
- Vendor Lock-in: Each cloud service vendor provides a slightly different platform, making it challenging to transfer from one to another after you’ve become acquainted with their services.
- Limited Control: Cloud services are fully owned and managed by the vendor, which means users will have less control over underlying hardware when using cloud infrastructure.
- Security: Even though one of the pros of cloud computing is improved security, that doesn’t mean that hackers won’t be able to penetrate these defenses and access data. Many organizations are understandably wary about handing over sensitive data to cloud vendors.
- Unforeseen Costs: Cloud services can bring cost savings, but our research also shows that users must watch out for cost creep and hidden fees. Pay-as-you-go is excellent, but don’t forget to switch off that EC2 instance if you’ve finished using it!
- Integration Complexities: Integrating cloud computing with any existing systems requires careful planning to make all the puzzle pieces fit without issue. This is particularly necessary for hybrid solutions and organizations using legacy systems like tape drives.
What Is The Future of Cloud Computing?
In its yearly forecast, Gartner states that global cloud spending will reach $600 Billion in 2024, up from $490 Billion in 2022. With such increased spending and investment, many more end users will see the benefits of the cloud.
Another Gartner report by David Smith and Dennis Smith also explores the idea that by 2027, Cloud Computing would have shifted from being a technology platform or system to the pervasive computing style of the time.
This research states that beyond serving the purpose of delivering data and applications, cloud computing may also play a key role in driving innovation.
After all, cloud computing is already at the center of some of the emerging tech today, such as IoT (Internet of Things) services, quantum computing, machine learning, artificial intelligence, and more.
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
With ML and AI being two of the hottest cloud trends in 2024, it’s unsurprising that cloud vendors are continuing to invest further in both machine learning and AI. After all, 2024 has almost been the year of AI so far, with tools like ChatGPT disrupting the way that we all search for information.
The big three believe that future growth may result from the increasing demand for their AI-based services, as shown by Microsoft's investment in OpenAI and Google’s generative AI language models, which now include their answer to ChatGPT, Google Bard.
Our research also shows that companies providing machine learning and AI services are shifting to the cloud because it can provide near-infinite scalability and resources. Needless to say, it’s very likely that we’ll continue to see the symbiotic relationship between ML/AI and cloud computing strengthen in the coming years.
Continued Growth of Hybrid Solutions
It’s also likely that we’ll continue to see large legacy organizations adopt cloud computing via hybrid solutions that mix both on-premise and cloud-based infrastructure.
While we’ve spent the majority of this article praising the cloud, for some, a fully cloud-based approach may not be suitable. This may be down to a shortage of skilled staff, security concerns, regulation issues, compatibility issues with legacy systems, and more.
That said, a hybrid solution can allow organizations to harness the power of the cloud without fully committing to a cloud setup. In doing so, they can reap the benefits of agility, scalability, and cutting-edge managed services without having to extend their own infrastructure investment.
Final Thoughts
Cloud computing has revolutionized many of the ways that we approach modern computing. And while the benefits of cloud technology will be unique in some way for each end user, this article has focused on the top 10 benefits of cloud computing in 2024.
Whether you’re enticed by improved accessibility and collaboration, significant cost savings, or increased reliability and disaster recovery, cloud computing offers a tremendous amount of potential to all of us, whether as an individual, start-up, or multinational organization.
That’s not to mention that cloud computing has been and will continue to be instrumental in accelerating innovation as a platform for rapid deployment and experimentation. So if you relish the idea of quickly testing and implementing new ideas, products, and services, ultimately driving innovation for all of us, cloud computing offers a natural synergy.
What do you think the future holds for cloud computing? Let us know in the comments below!
Looking for ways to enhance your career as a cloud professional? Check out:
The Top Microsoft Azure certifications
People are also reading:
