Selenium Automation Testing has become very popular among testers because of the various advantages it offers. When we talk about automation testing, the first thing that often comes to mind is our favorite automation testing tool. However, it won the hearts of many testers and developers with its simplicity, availability, and ease of use. With its advent in 2004, Selenium made the life of automation testers easier and is now a favorite tool for many automation testers. So, without further delay, let’s get to know what is Selenium testing and how it helps in automation testing.
What is Selenium?
Selenium was invented with the introduction of a basic tool named as “JavaScriptTestRunner”, by Jason Huggins at ThoughtWorks to test their internal Time and Expenses application. Now it has gained popularity among software testers and developers as an open-source portable automation testing framework. It has the capability to automate browsers with specific browser bindings for automating web applications for testing purposes. It is a suite of four tools designed for different purposes. Let’s get to know about Selenium in detail and the different tools that it offers.
Selenium Suite of tools
It has 4 major components with a different approach for automation testing which is popular as the Selenium suite of tools. Every software tester or developer chooses tools out of it depending upon the testing requirement for the organization.
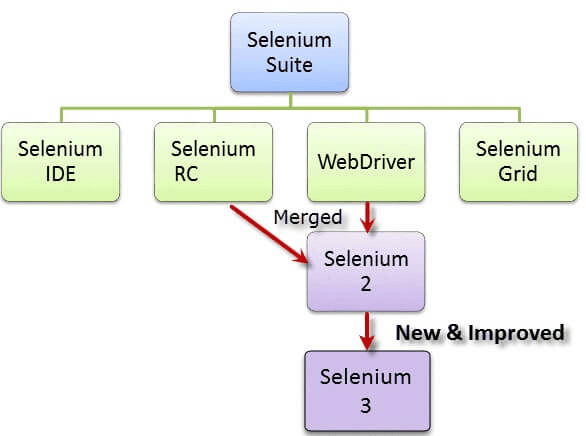
Selenium RC (Remote Control)
Selenium Core was the first tool in the Suite of tools. However, it was deprecated as it had some issues related to cross-domain testing because of the same-origin policy. So, to overcome that Selenium Remote Control (Selenium RC) was introduced after Selenium core. RC turned out as an aid to the cross-domain issue. RC has an HTTP proxy server which helps in befooling the browser into believing that both the Selenium core and Web app which is being tested are from the same domain hence removing the cross-domain issue.
Selenium RC is divided into two parts which help in overcoming the cross-domain issue:
- Selenium Remote Server
- Selenium Remote Client
But the major issue with RC was the time taken to execute a test. As the Selenium server communicates using HTTP requests, it was more time-consuming. Because of this limitation, RC also is now not much in use.
Selenium IDE
We also discussed the Selenium IDE. This was earlier known as Selenium recorder, and it's a tool used to record, edit, debug, and replay functional tests. With the Selenium IDE plugin, you can record and export tests in any of the supported programming languages like Ruby, Java, PHP, Javascript, etc.
Selenium Grid
Selenium Grid is based on Hub-node architecture. With Selenium Grid, you can run parallel test sessions across different browsers. Hub controls Selenium scripts running on different nodes(specific browsers inside an OS) and test scripts running on different nodes can be written in any programming language.
Selenium Grid was used with RC to test multiple tests on remote machines. Nowadays, as people find Webdriver better than RC, hence Grid works with both Webdriver and RC.
Selenium Webdriver
Selenium Webdriver is an enhanced version of Selenium RC and the most used tool. It accepts commands via client API and sends them to browsers. Simply put, Selenium Webdriver is a browser-specific driver that helps in accessing and launching the different browsers. It provides an interface to write and run automation scripts. Every browser has different drivers to run tests.
- Mozilla Firefox uses Firefox Driver (Gecko Driver)
- Google Chrome uses Chrome Driver
- Internet Explorer uses Internet Explorer Driver
- Opera uses Opera Driver
- Safari uses Safari Driver and
- HTM Unit Driver used to simulate browsers using headless browser HtmlUnit
Selenium Client API
It is the latest tool in the Suite of tools. With Selenium Client API you can write test scripts in various programming languages instead of writing test scripts in Selenese. Selenium client API is available for Java, JavaScript, C#, Ruby, and Python. These scripts can communicate with Selenium with predefined commands and functions of Client API.
Why Selenium for Automation Testing?
Since we are now familiar with Selenium and its suite of tools, let’s find out the various benefits of Selenium which make it stand from the crowd as a tool for automation testing:
- Open-Source tool: Since it is an open-source tool, it doesn’t require any licensing costs which give it an upper hand over other automation testing tools.
- Tool for every need: As mentioned earlier, Selenium has a suite of tools, so it suits every need of the users. You can use various tools like WebDriver, Grid, IDE for fulfilling your different needs.
- Supports all major languages: The major challenge that a tester or developer faces with an automation testing tool is the support for languages. Since selenium supports all major languages like Java, JavaScript, Python, Ruby, C sharp, Perl, .Net and PHP, it is easier for testers to use.
- Browser and Operating System support: Selenium supports different browsers like Chrome, Firefox, Opera, Internet Explorer, Edge, and Safari and different operating systems like Windows, Linux, Mac. This makes it flexible to use.
- Community Support: Selenium has an active open community that helps you solve your issues and queries related to it. This makes it the best choice as your automation testing tool.
Here’s a quick comparison table of Selenium with other available tools:
| Features | Selenium | QTP | RFT |
| Open Source | Yes | No | No |
| Support | Open Source Community | Dedicated Support | Dedicated Support |
| Coding Skills Required | Yes | No | No |
| OS Support | Windows, Linux, Mac | Windows | Windows |
| Languages Supported | Java, JavaScript, Python, Ruby, Perl, .Net, C sharp | VB Script | Java and C sharp |
Selenium Webdriver and its architecture
Since Selenium WebDriver is the most used tool, so we’ll be using the same to execute Selenium test cases. To understand the complete process on a very simple level, Selenium WebDriver Architecture consists of:
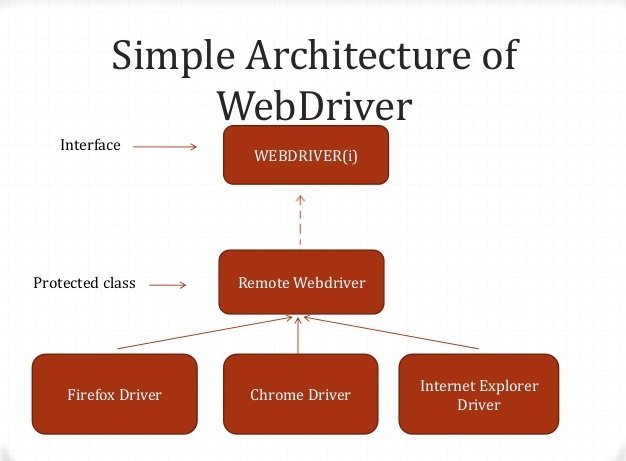
Basically, the Selenium web driver works in three layers: Browser Driver, Remote Driver, and Language Bindings.
Core components of WebDriver Architecture:-
- Selenium Client Library / Language Bindings
Selenium bindings / Client libraries are created by developers to support multiple programming languages. For instance, if you want to use the browser driver in Python, use the Python bindings. You can download all the bindings on the official Website.
- JSON Protocol over HTTP
JavaScript Object Notation is used as a data transfer protocol to send data from a server to a client on the web. With JSON, it is very easy to write and read data with data structures like Array and Object support. This wire protocol provides a transport mechanism and defines a RESTful web service using JSON over HTTP.
- Browser Specific Driver
Each web browser has a specific browser driver for Selenium bindings. The browser driver accepts commands from the server and sends it to the browser without the loss of any internal logic of browser functionalities. Browser drivers are also specific to programming languages like Ruby, C#, Java, etc for web automation.
Following are the steps when we run any test script using Webdriver:
- HTTP request gets generated for every Selenium command and sent to browser driver.
- A specific browser driver receives the HTTP request through the HTTP server.
- HTTP Server sends all the steps to perform a function which are executed on the browser.
- The test execution report is sent back to the server and the HTTP server sends it to the Automation script.
- Browsers
Selenium Webdriver supports all the major browsers like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Internet Explorer and Safari browsers.
Setting up Selenium on your Local Machine
Let’s understand the steps of how we can configure Selenium in your local machine and running a test in your local browser.
Note: We’ll be using the IntelliJ code editor for writing Automation script.
- Download and install Java Runtime environment in your local system.
- Download Java Development Kit
- Download and install all Java Selenium Files (Selenium Server Standalone)
- Install Browser Specific Drivers ( In this blog, we’ll perform Automation on Chrome, so Chrome Driver for this case)
Sample Selenium Script for Web Automation
Here is the sample automation script which can be run to automate the testing process on the local chrome browser. Since we are using IntelliJ as our code editor, so we’ll write the same in IntelliJ.
Sample Script
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
public class TestSelenium {
public static void main(String[] args){
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver","C:\\Users\\Admin\\Desktop\\LT Automation\\chromedriver_win32\\chromedriver.exe");
WebDriver driver= new ChromeDriver();
driver.get("https://hackr.io/");
try {
WebElement signup = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id="navbarCollapse"]/ul/li[2]/a"));
signup.click();
WebElement login= driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id="modalSignUp"]/div/div/div/div/div[4]/p/a"));
login.click();
String windowHandle = driver.getWindowHandle();
WebElement TextBox = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id="login-modal-form"]/div[1]/div/input"));
TextBox.sendKeys("sample-email@lambdatest.com");
WebElement Password = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id="login-modal-form"]/div[2]/div/input"));
Password.sendKeys("sample-password");
WebElement proceed = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//*[@id="login-modal-form"]/div[4]/button"));
proceed.click();
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
This code will launch a website(here https://hackr.io/), find “Signup/Login” element, click on the Signup/login button, then go to the login page by finding “Login”. After that will enter the credentials to the login page and click the login button and redirected to Hackr.io homepage.
Online Selenium Grid
The major challenge in running Selenium on a local machine is the limited number of browsers in the local machine. Since you can have only one version of a particular browser installed in your local machine so if the need comes to test on some downgraded or upgraded version of that browser, you’ll need to upgrade or downgrade the already installed browser in your local machine. Also, you can install only a specific number of browsers in the system. So, if the need comes it becomes almost impossible to test across all browsers and operating systems. Hence an online Selenium grid can help.
With the help of an online selenium grid on the cloud, you can test across all the browsers, browser versions, operating systems, resolutions for cross-browser compatibility. Online platforms which provide selenium grid-like LambdaTest, SauceLabs, BrowserStack can help you perform cross-browser tests on cloud grid of various browsers-OS combinations.
Common Selenium command and operations
While writing an automation script, you will be using many repeated commands and doing various operations. Let’s have a quick look at the most common and used commands in Selenium automation testing.
Page Visit:- The first thing to do visit a webpage to start automation testing.
driver.get("https://hackr.io/");
Find an Element:- Find elements to automate them.
// find just one, the first one Selenium finds WebElement element = driver.findElement(locator); // find all instances of the element on the page List elements = driver.findElements(locator);
Actions on Elements:- Work on found elements.
// chain actions together driver.findElement(locator).click(); // store the element and then click it
WebElement element = driver.findElement(locator); element.click();
Multiple Element Commands:- Common commands to click, submit, clear, input etc.
element.click(); // clicks an element
element.submit(); // submits a form
element.clear(); // clears an input field of its text
element.sendKeys("input text"); // types text into an input field
Question Commands:- Check conditions for elements.
element.isDisplayed(); // is it visible to the human eye? element.isEnabled(); // can it be selected? element.isSelected(); // is it selected?
Get your Info:- Commands for retrieving information for an element.
// directly from an element
element.getText();
// by attribute name
element.getAttribute("href");
To Sum Up
Selenium is one of the best automation testing tools which can be used to automate web browser interactions. You can perform automation testing by writing code in any of your preferred language supported by Selenium and can easily run your automation script to automate testing of an application or a process. Its ease of use makes it different from other tools and with the help of an online grid you can even run your tests in parallel across more than one browser. So, what are you waiting for? Write a beautiful automation Script and test your website! If you have any questions, let us know in the comments section below.
Happy Testing!
People are also reading:
- What is Selenium IDE?
- What is Selenium WebDriver?
- Best Selenium Testing Interview Questions
- Best Web Development IDE
- Security Testing Tools
- Best Software Testing Courses
- What is Software Testing Life Cycle?
- Types of Software Testing
- Manual Testing Interview Questions
- Security Testing Tools
- Best Software Testing Certifications
- Best Software Testing Certifications








